Add New Redirect Rule
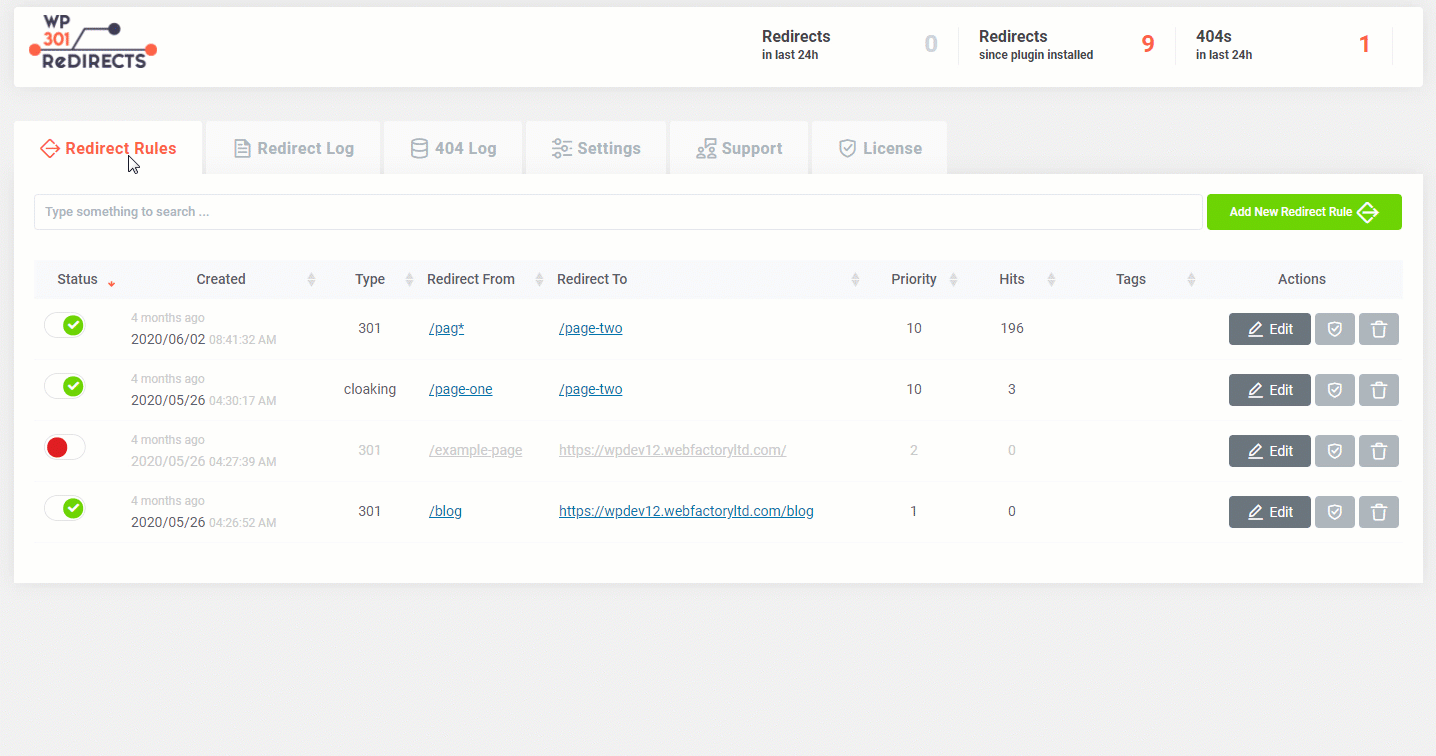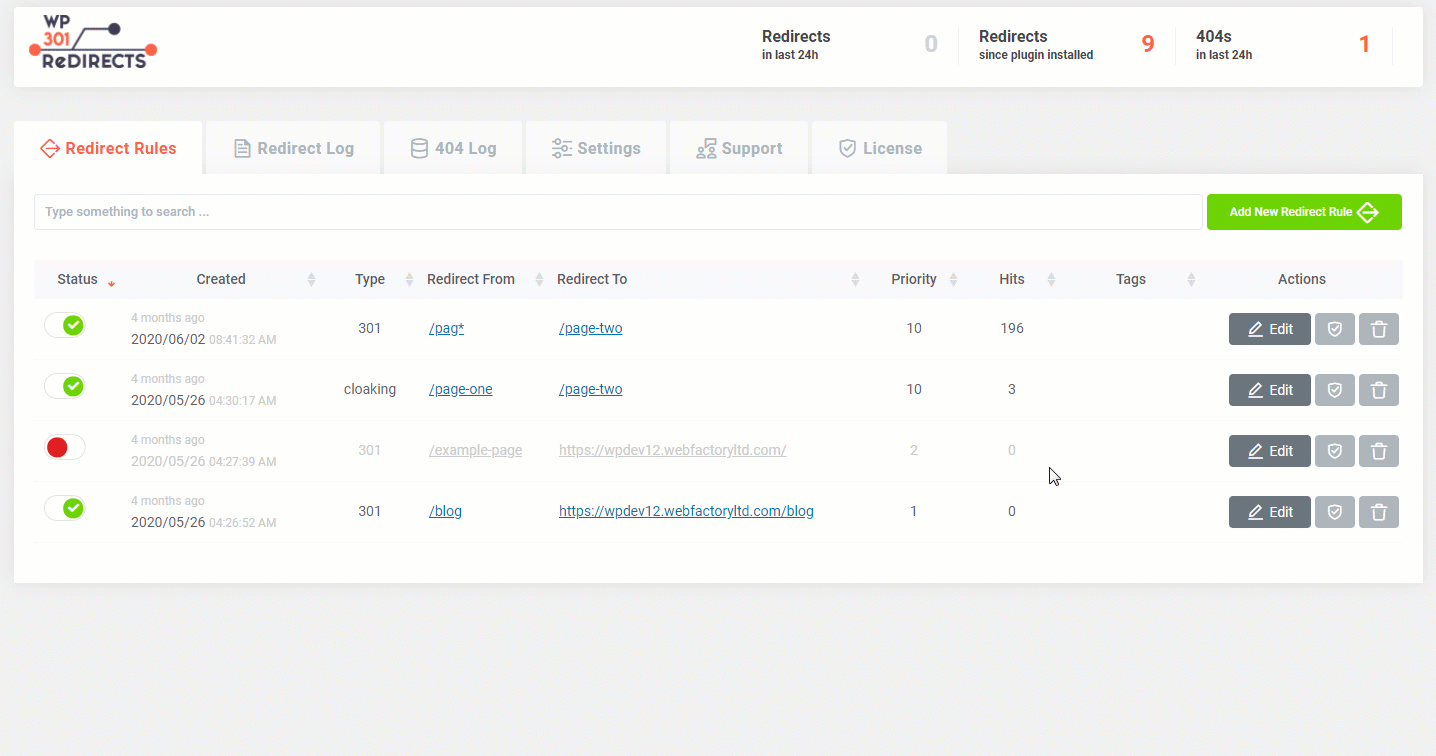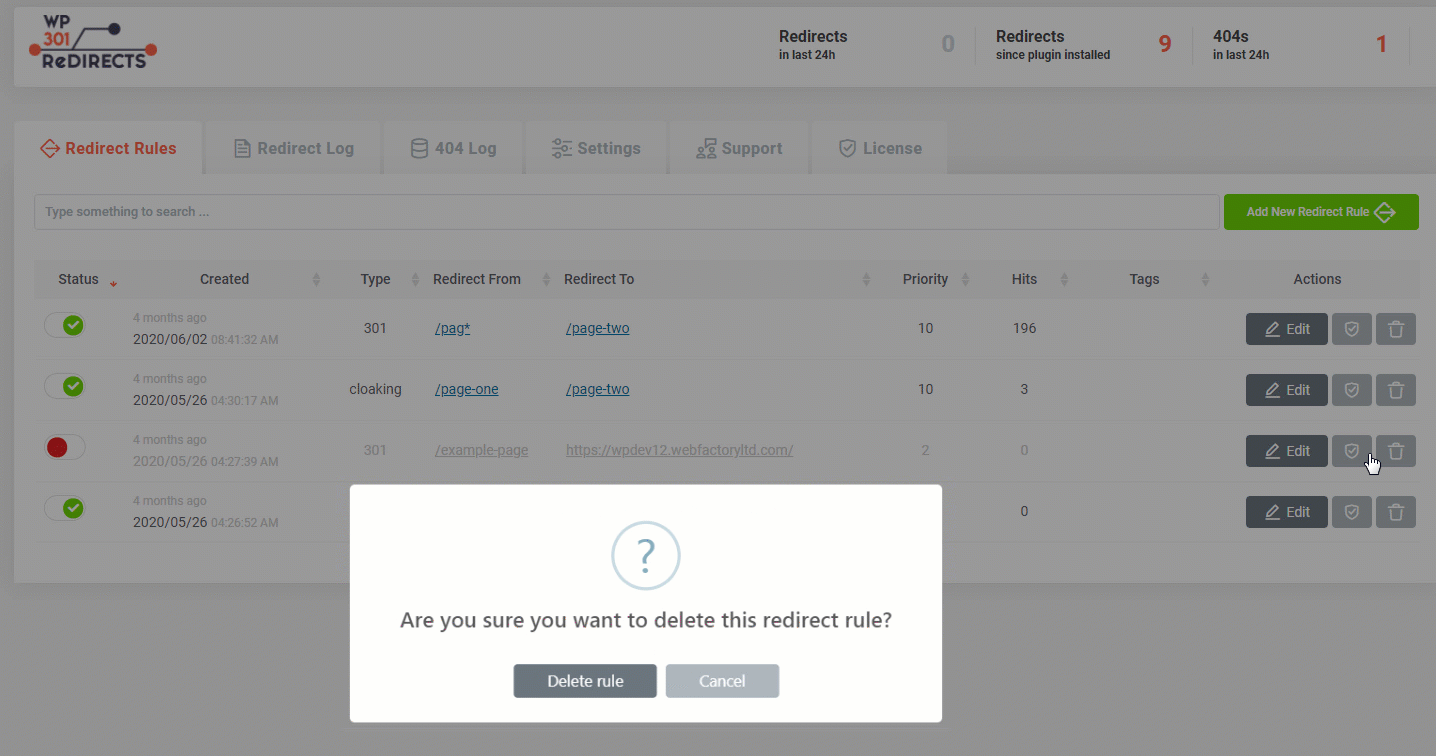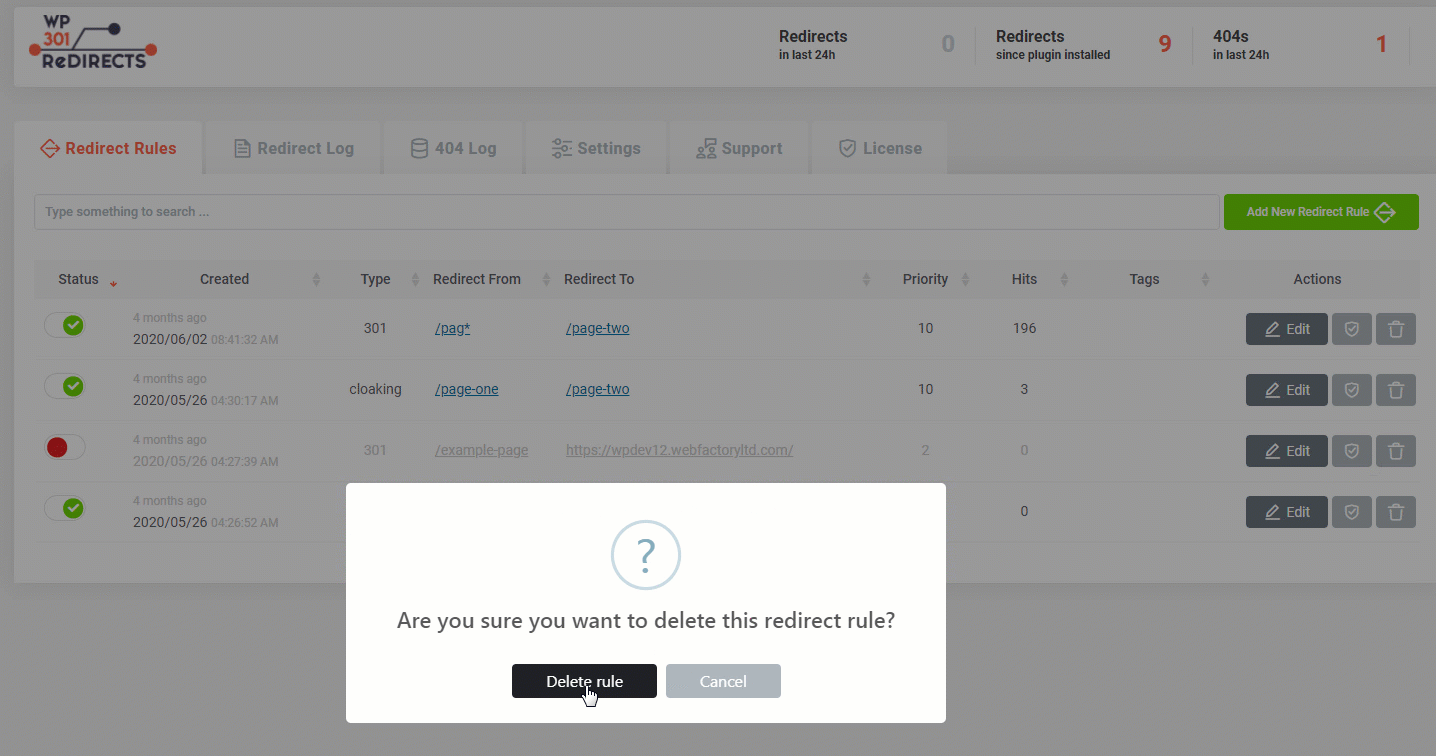
Redirect Rules allow you to quickly & easily transfer traffic from one source to another. Usually, this is used to avoid 404 errors. But you’re allowed to redirect any page from your site to any other source from your own domain, or you can point it to an outside source of your choice.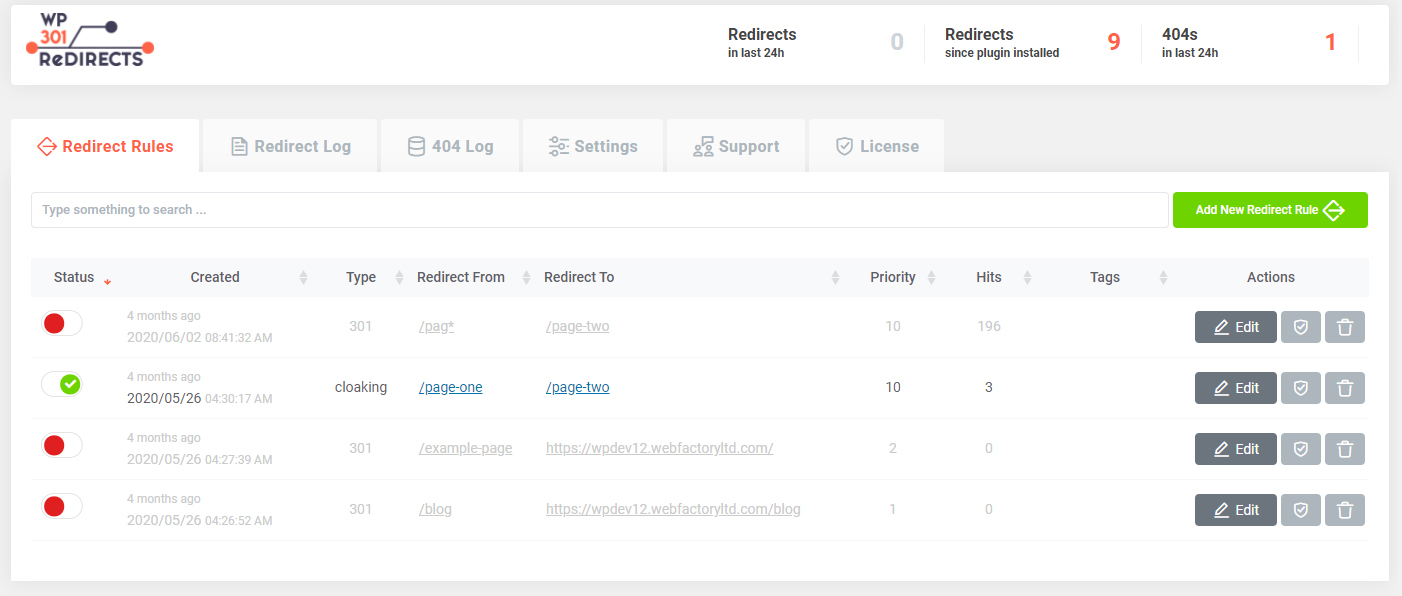 In order to add a new redirect rule, please follow these steps:
In order to add a new redirect rule, please follow these steps:
- Go to Settings -> WP 301 Redirects
- Open the first “Redirect Rules” tab
- Click on the “Add new redirect rule” button
This will open a new window that holds all the settings & options you will need for setting up the redirect.
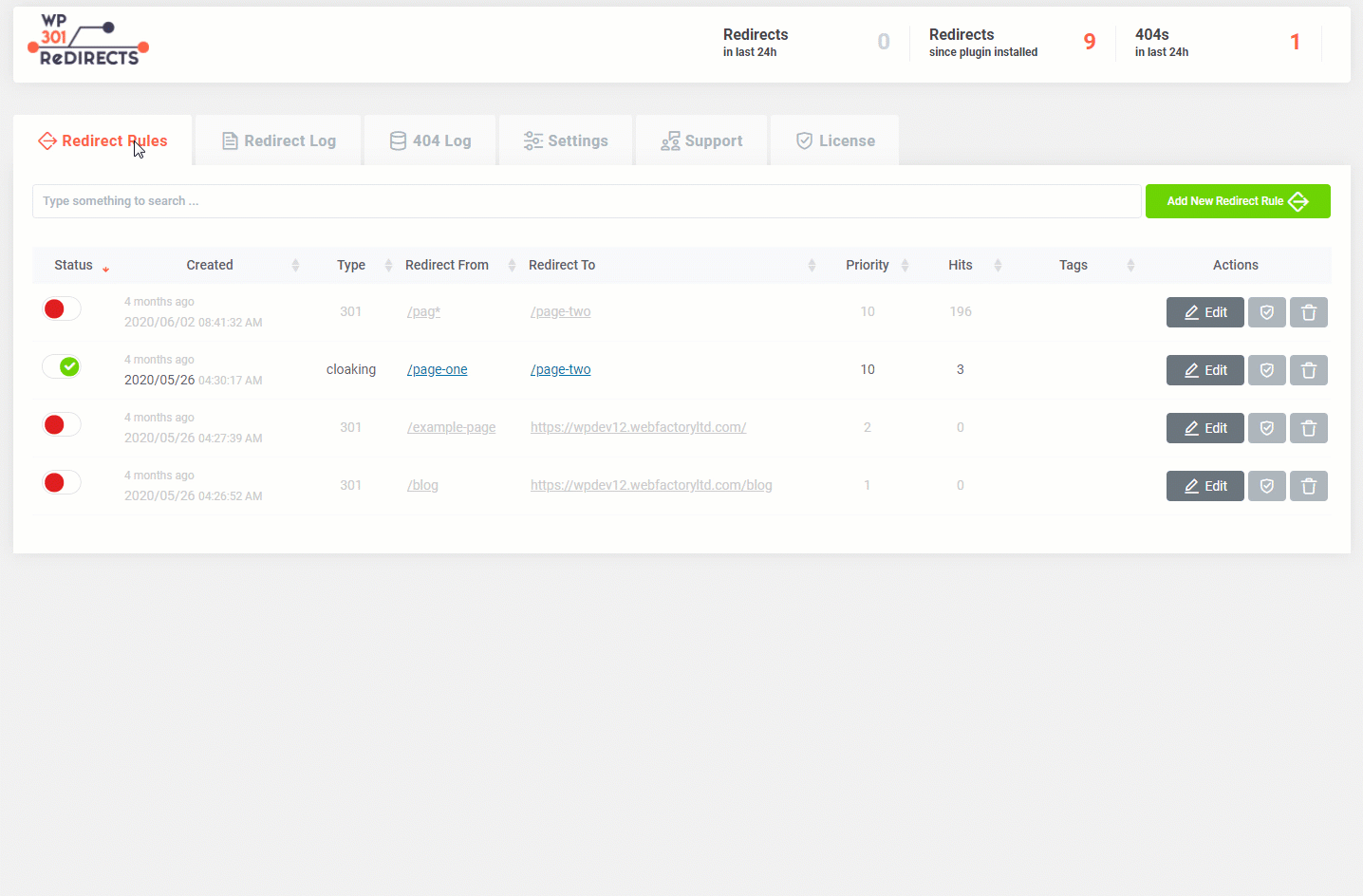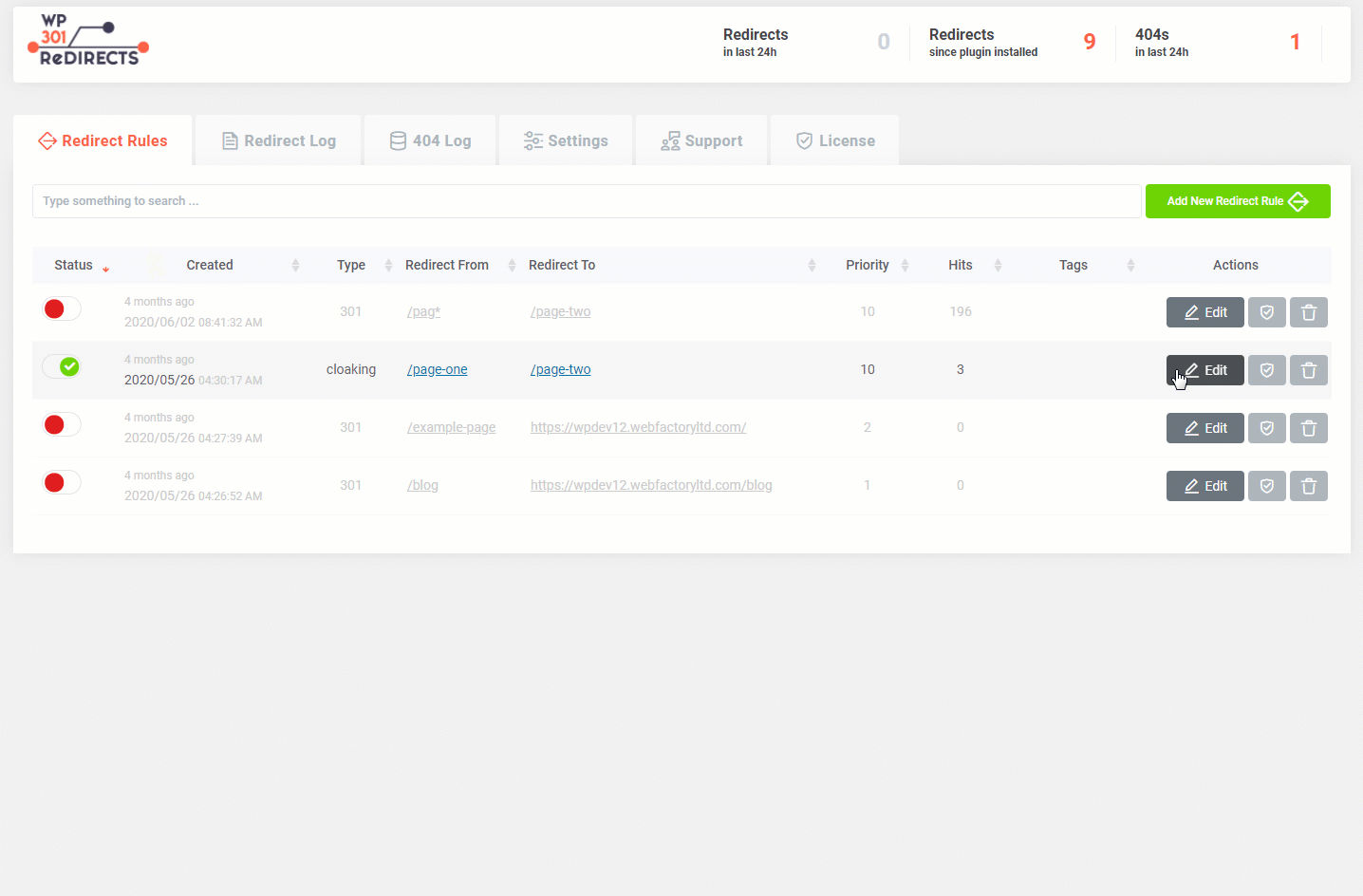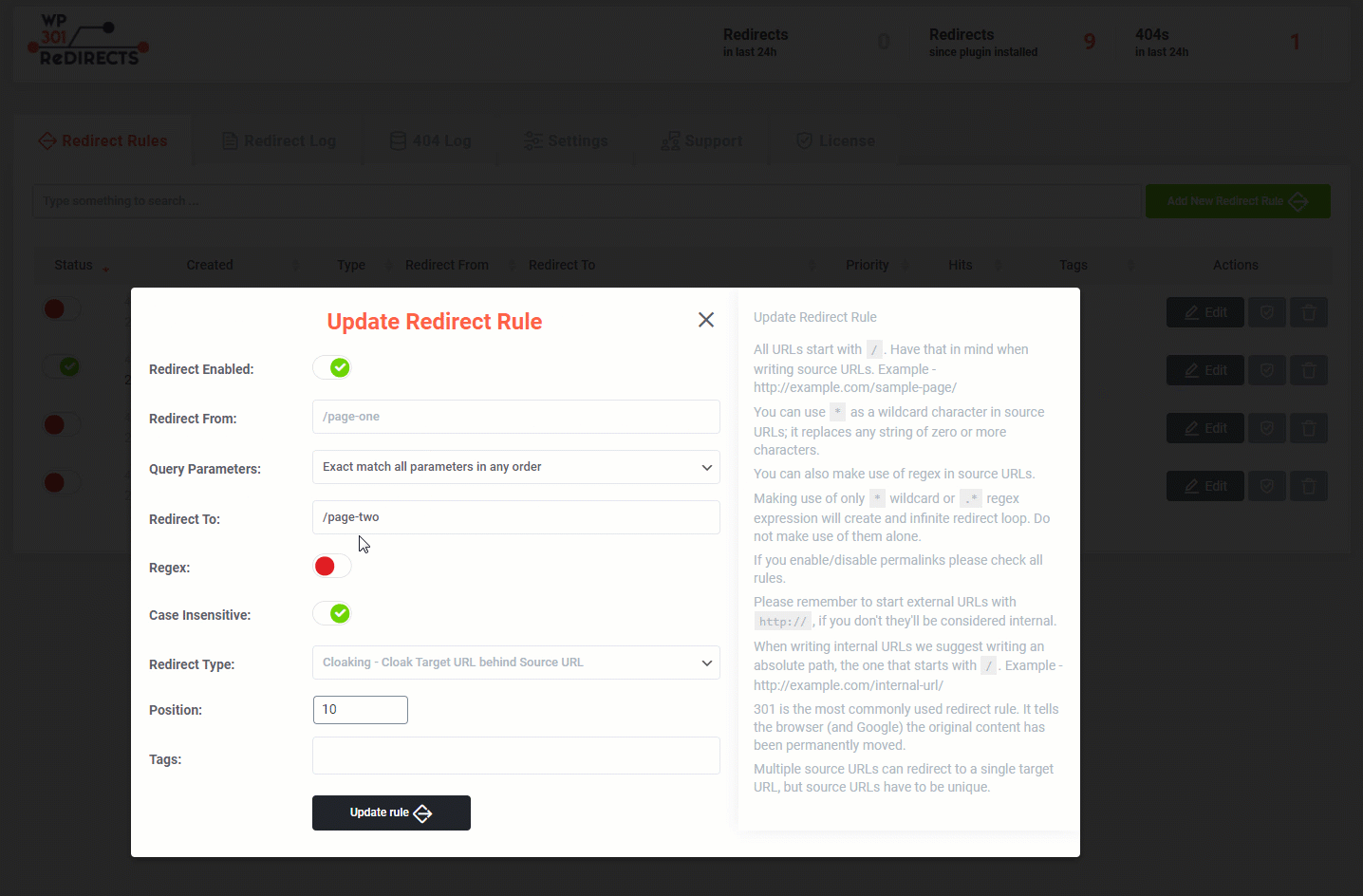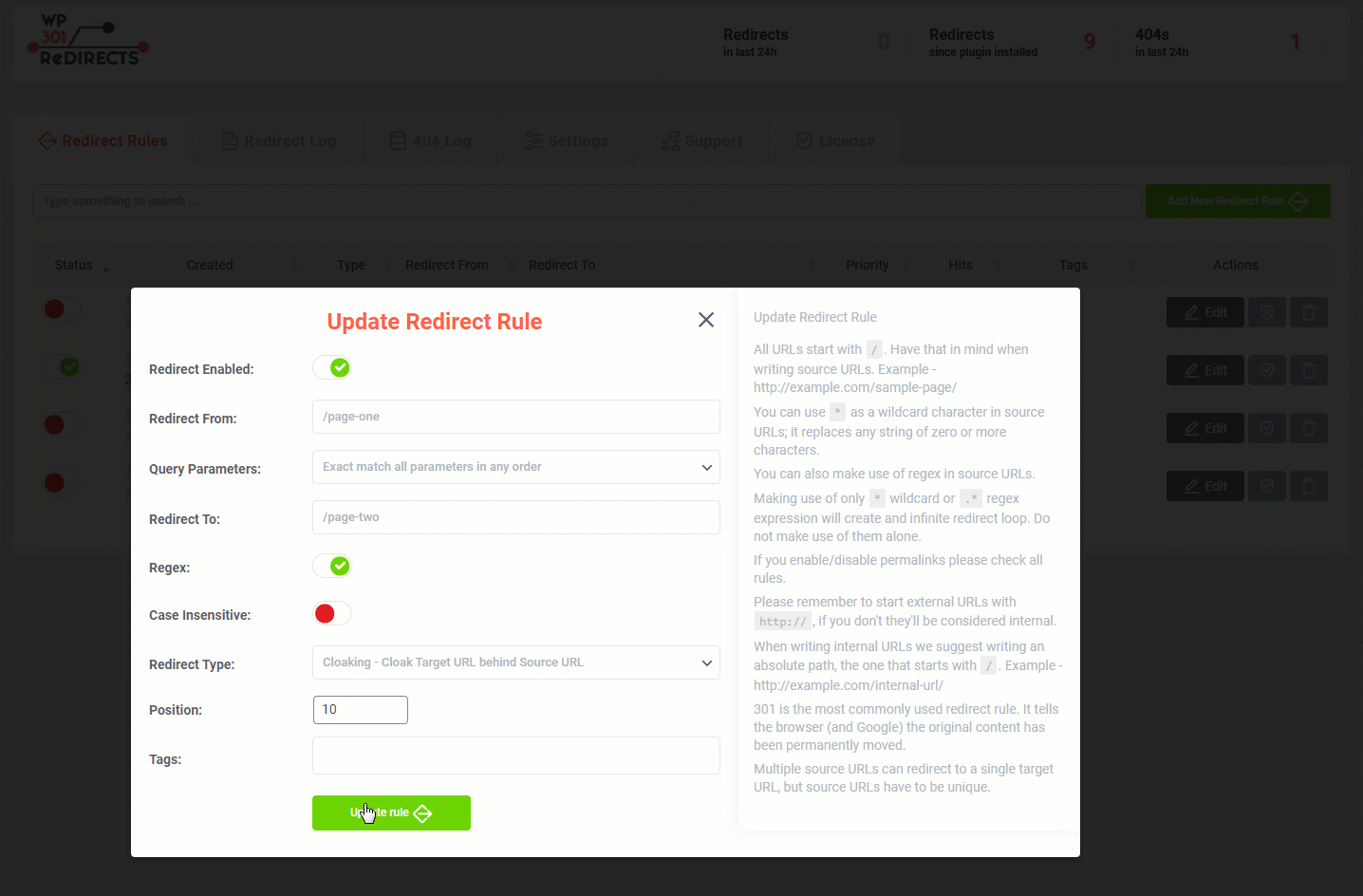
Redirect Enabled
Turn on (green) if you want the redirect to start working immediately after you click the “Add rule” button or turn off (red) if you want to enable it at a later point.
Redirect From
The plugin will write down the domain name of your site, where you just need to add the relative URL.
For example, you will have the https://yourdomain.com/ already written, and all you have to do is type in the rest of the URL you want to redirect.
Example: Let’s say that you have a blog at https://yourdomain.com/blog and you want to redirect it somewhere else. Since the plugin will have the https://yourdomain.com/ part already there, simply write down ‘ blog’ in the “Redirect From” field.
Query Parameters
You have already seen query parameters are, but you are just not aware of that. Query parameters are all those variables that you see after a link. Those are added after the question mark symbol (?) and are used to pass an additional value to the URL. The most common use is adding a UTM tag at the end of the link that allows you to track visits to your site via Google Analytics. Another common use is affiliate links that need specific ID numbers added to them. Here’s an example: https://www.yoursite.com/blog?utm_campaign=name&utm_medium=email where a query parameter is ?utm_campaign=name&utm_medium=email Depending on what you want to do when redirecting, you can ignore those parameters, match them exactly in any order, or ignore & pass parameters to the target.Ignore all parameters
Check if you do not want the WP 301 Redirects to take query parameters into consideration. If checked, the plugin will ignore all the parameters that are displayed after the question mark. For example, let’s say that you have an affiliate link with your affiliate ID attached to the URL like mywebsite.com/affiliate-landing/?aff=123 that you want to redirect to a new URL. If you ignore all parameters, that means that this link would be recognized as mywebsite.com/affiliate-landing/. So no matter which affiliate link gets opened, it would be redirected to a new location.Exact match all parameters in any order
In cases where you want to make sure that all parameters are present, but you do not care in which order, you should select this option. For example, mywebsite.com/affiliate-landing/?aff=123&source=facebook and mywebsite.com/affiliate-landing/?source=facebook&aff=123 will both be triggered by the redirect rule since they’re basically the same thing.Ignore & pass parameters to the target
In cases where you need to keep the query parameters as part of the new redirected URL, check this option. For example, if you redirect mywebsite.com/affiliate-landing/?aff=123 to mywebsite.com/new-landing/, the “Ignore all parameters” (the first one of the options would actually ignore all parameters and redirect to mywebsite.com/new-landing/. But this “Ignore & pass parameters to the target” option would pass the parameters to the new URL and would redirect to mywebsite.com/new-landing/?aff=123Case Insensitive
When it comes to domain names, it is important to know that those are not case-sensitive. That means that https://wp301redirects.com and https://WP301REDIRECTS.COM is the same exact thing, and no matter how you type it, you will end up on the same website. But it’s also crucial to understand that everything that goes after the domain name & the top-level domain can be case-sensitive. So, in the same example, https://wp301redirects.com/blog is not the same as https://wp301redirects.com/BLOG. While this is technically true, please note that most of the modern hosting services usually treat this kind of URLs as the same. So, in the example before, you would still end up on the same page. However, this depends on the servers and what you want to do. Because of that, when doing a redirection, you can set the URL to be case insensitive or vice versa. Default: “On”Redirect Type
Not all redirects are the same. While the most common one is a 301 redirect, there are situations in which you will need to return a specific status code.- 301 Redirect – a permanent redirect. Used when the old URL does not exist anymore or when you want to move to another location permanently. Browsers will cache this redirect and always open the new URL. Changing the rule will require clearing the browser cache of visitors.
- 302 Redirect – a temporary redirect. Used when a document is only temporarily unavailable and you plan to remove the redirect in the future. Browsers will not cache the redirect and will check each time if it is still active.
- 304 Redirect – not modified. It indicates that the resource has not been modified since the last request.
- 307 Redirect – temporary redirect, which guarantees that the method and the body will not be changed when the redirected request is made.
- 308 Redirect – a permanent redirect. Used when you want to make sure the redirected location uses the same exact request (for example, POST)
- Cloaking – hide target URL by Source URL
Position
The Position allows you to choose the order in which the redirection rules will get checked & executed.
For example, let’s say you have a redirect from mywebsite.com/old-landing/ to mywebsite.com/new-landing/ with the “Ignore all parameters” feature turned on. Then you decide to add a redirect from mywebsite.com/old-landing/?aff=123 to mywebsite.com/some-other-page/.
Unless you prioritize this second rule, that would mean that the first rule (that ignores the query parameters) would always be executed, and the second rule would never be triggered. You can fix that by adding a lower number to the rule you want to execute first (for example, for the rule you want to be checked first, add the number 10 and add the number 100 to the other one).
Update Redirect Rule
Sometimes, instead of creating a new redirect rule, you will want to update an existing one. Luckily, WP 301 Redirects allows you to do that quickly:- Go to Settings -> 301 Redirects
- Open the first tab, labeled “Redirect Rules”
- From the list, choose a redirect rule you would like to update
- On the far right side of the screen, find “Actions”
- Click on the first “Edit” icon
Using Tags in Redirects
Tags are a powerful feature that allow you to categorize and locate your redirects quickly. When creating or editing a redirect, you can add a tag that serves as a unique identifier, which can be used to filter and search through your list of redirects. This is especially useful when dealing with a large number of URLs, as it simplifies the management and tracking process. To streamline the management of your redirects, clicking on a specific tag will instantly filter and display all redirects that share that tag. This feature allows for quick access and organization of your redirects, making it easier to work with large sets of data.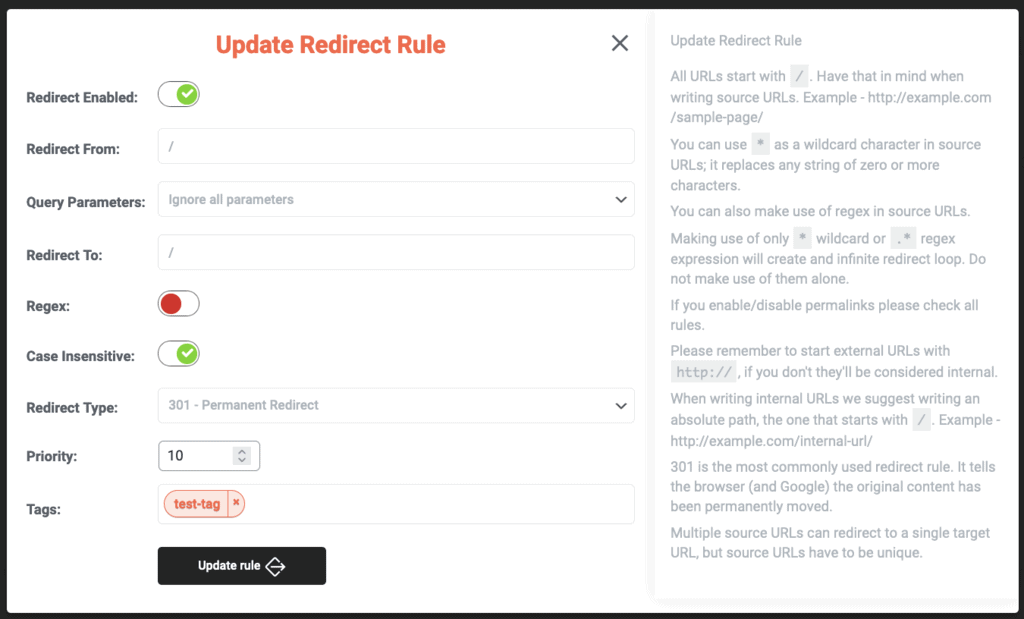
Check Redirect
When creating redirects, you will want to make sure that each redirect you set actually works properly. Redirecting from the source page will do the trick – sometimes, checking multiple redirects takes time. That’s why we included a simple button that will let you know the status of your redirect without you having to type in URLs.How to quickly check a redirect?
- Go to Settings -> 301 Redirects
- Open the first tab, labeled “Redirect Rules”
- From the list, choose a redirect rule you would like to test
- On the far right side of the screen, find “Actions”
- Click on the second icon (Shielded checkmark)
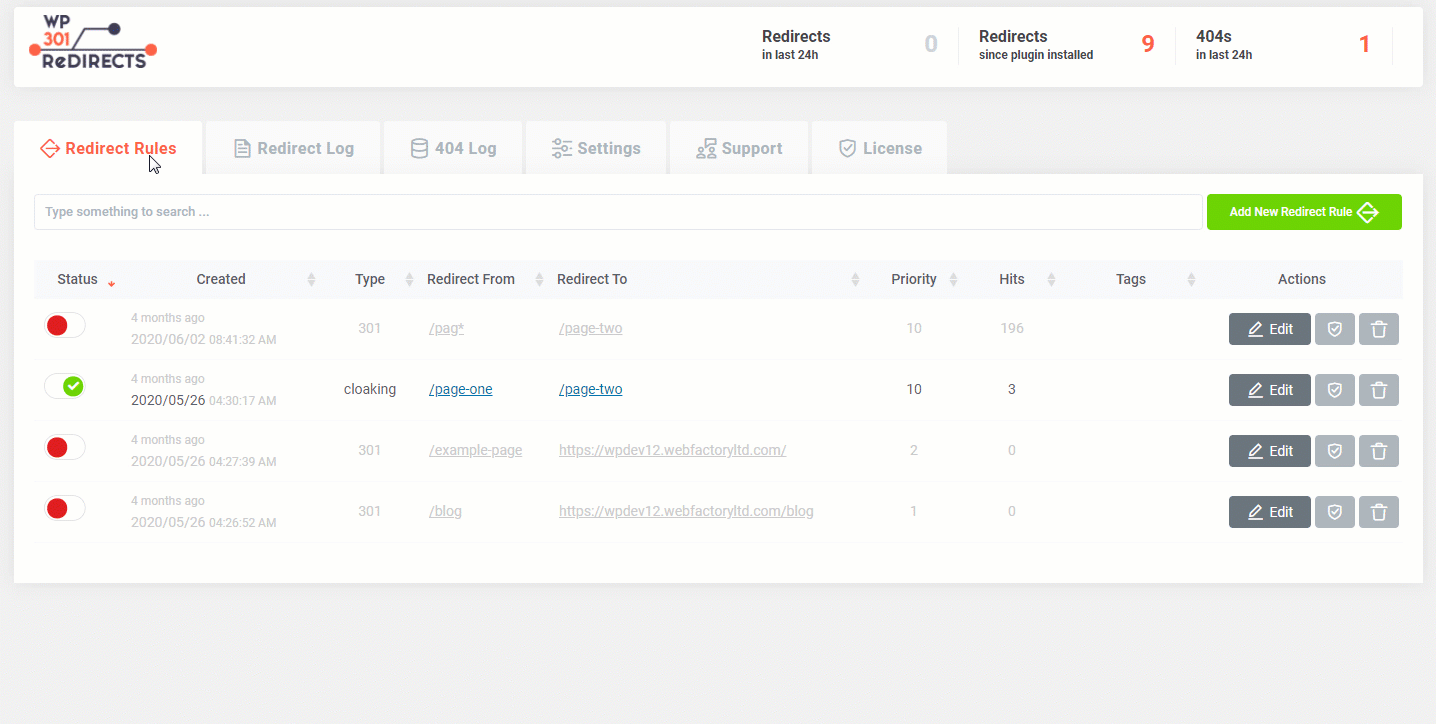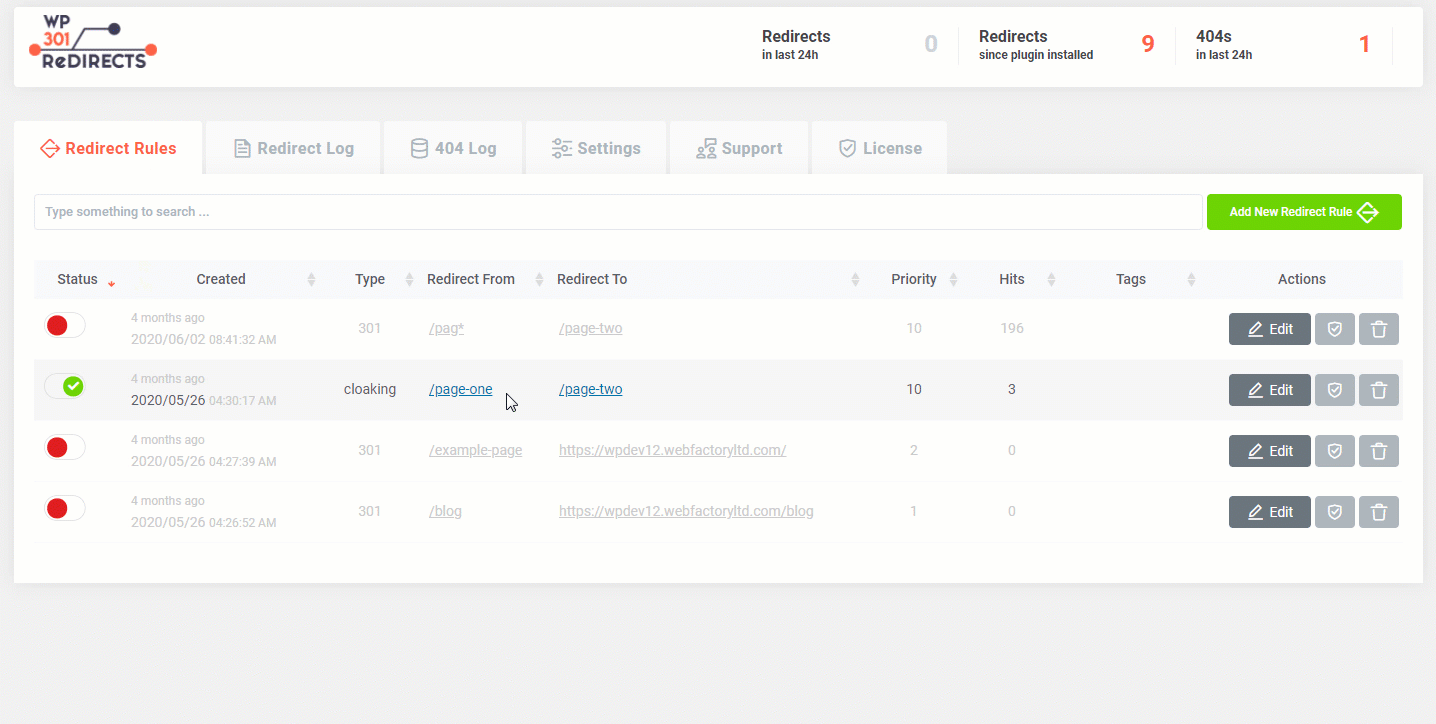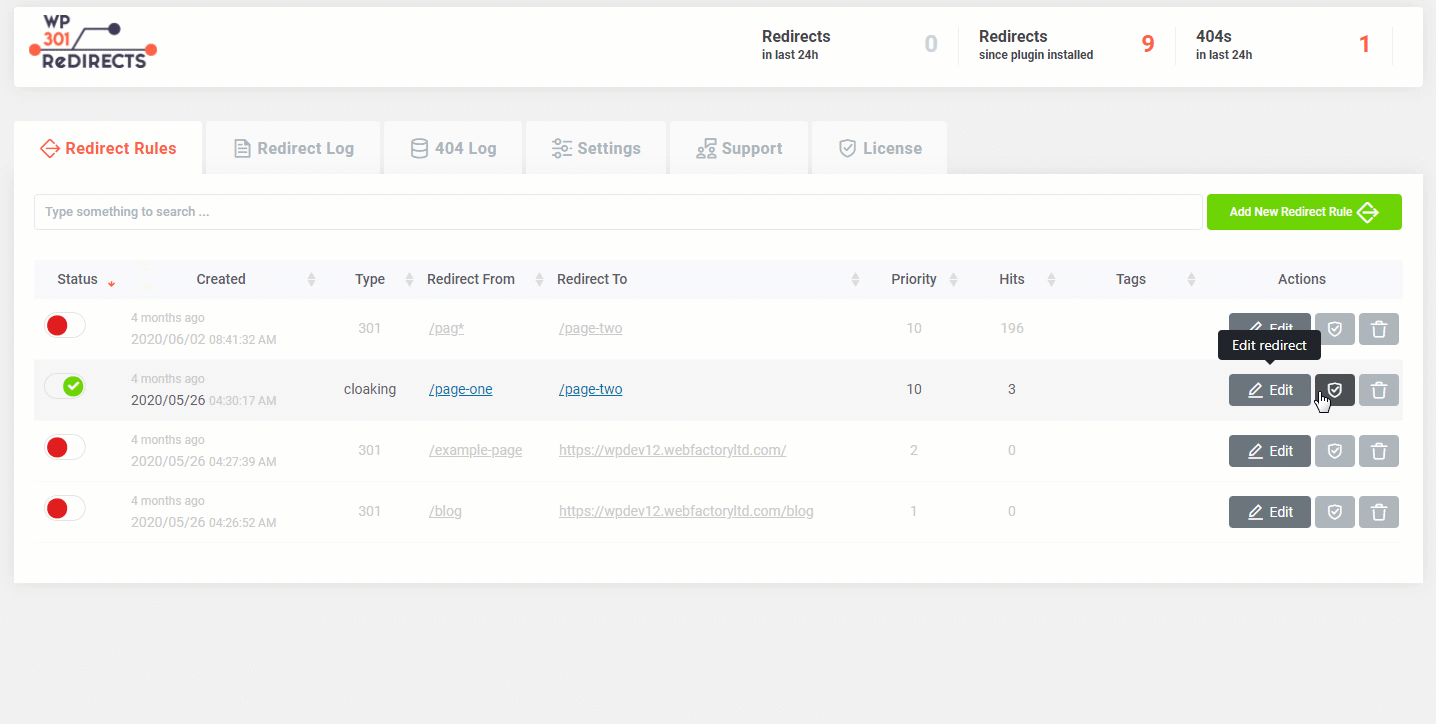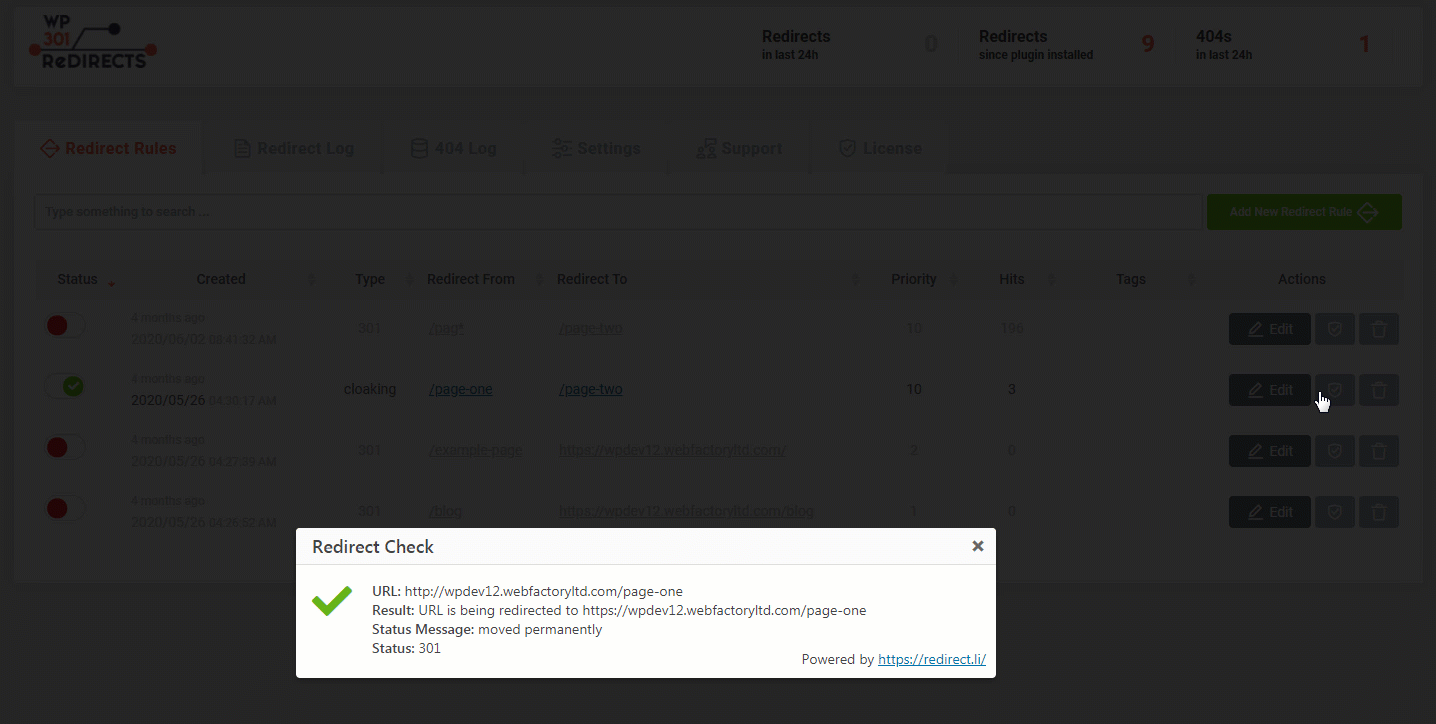 A new popup window will appear, showing you details about a redirect:
A new popup window will appear, showing you details about a redirect:
- URL: http://yourdomain.com/example
- Result: The URL is being redirected to http://yourdomain.com/new-example
- Status Message: moved permanently
- Status: 301
Search
Sooner or later, you will have more than just a few redirect rules you will have to handle for your WordPress site. When that happens, it may become difficult to find a specific redirect. To make it easier, we have added a search box on top of the Redirect Rules tab. Type in a part of the URL, and let WP 301 Redirects find your rule.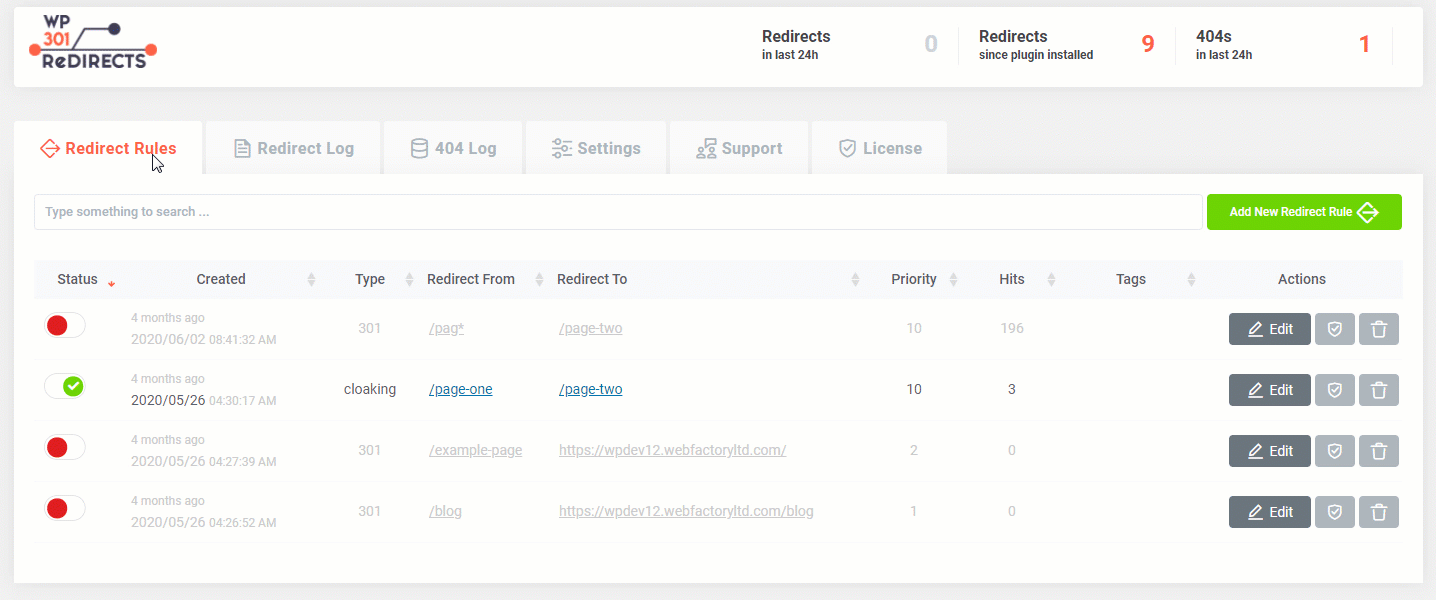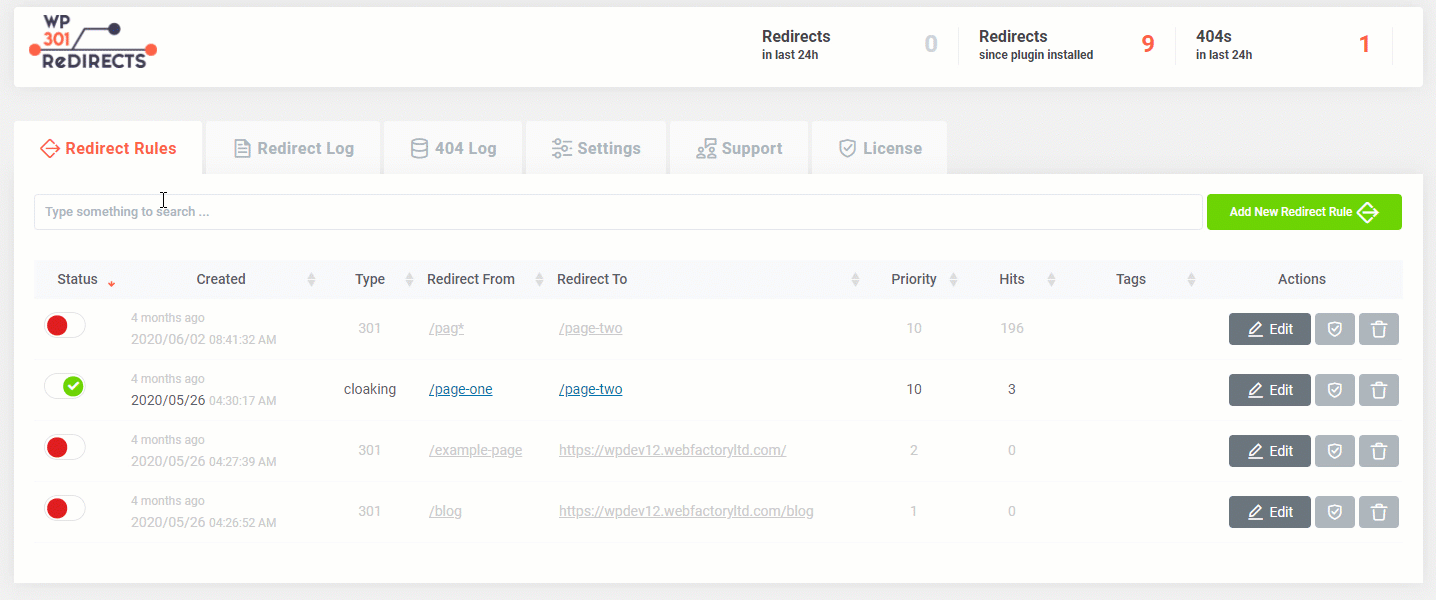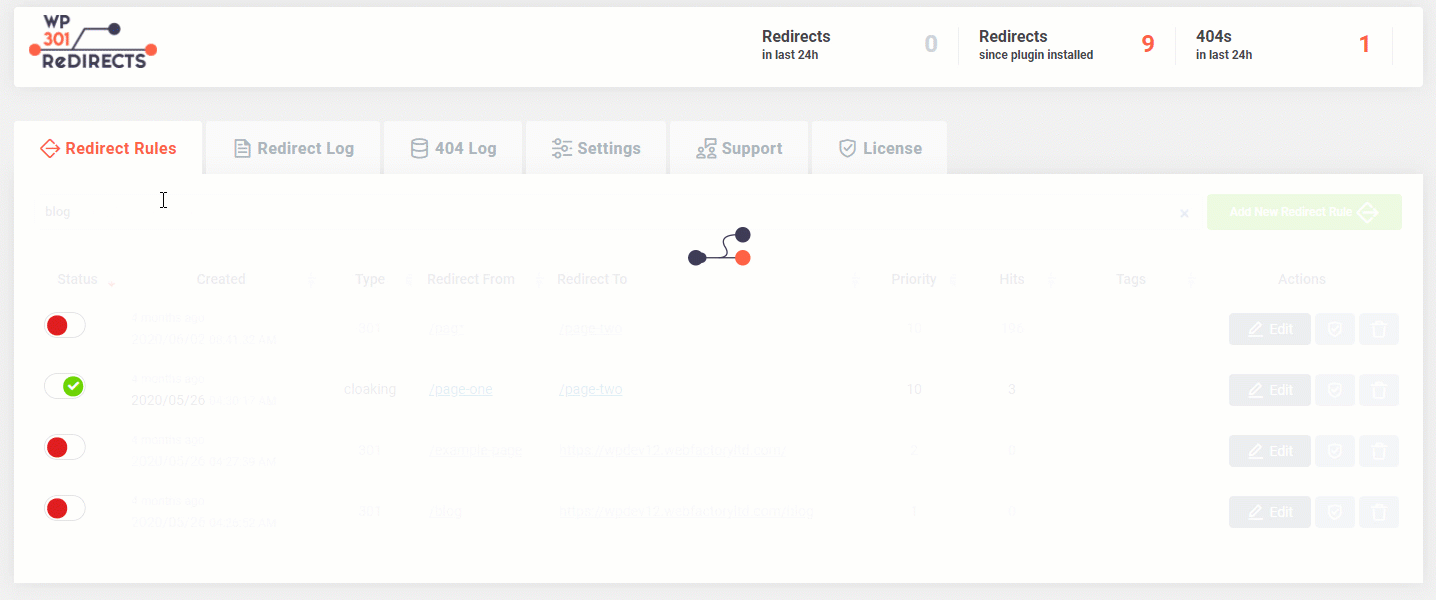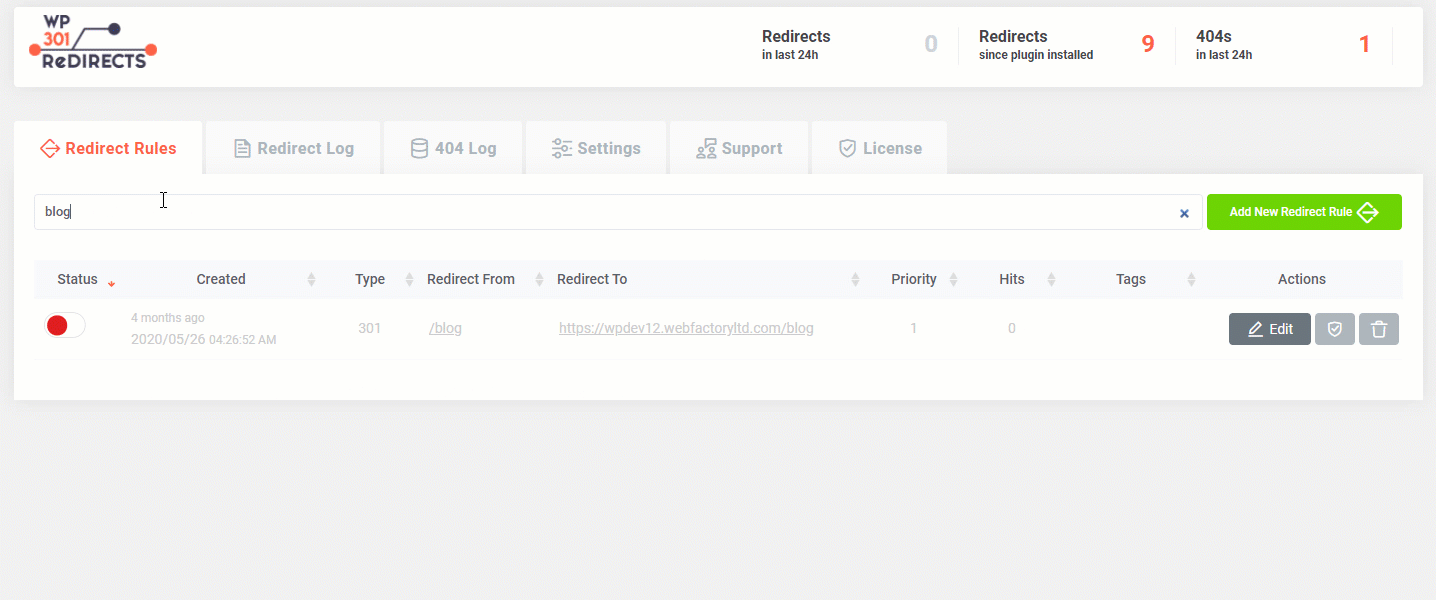
Delete Redirect Rule
When you decide that you no longer need a redirect rule, you can quickly delete it from WP 301 Redirects.How to delete a redirect rule?
- Go to Settings -> 301 Redirects
- Open the first “Redirect Rules” tab
- Find the rule you want to delete
- On the far right side of the screen, click on the trashcan icon
- Confirm you want to delete the redirect rule
This will permanently delete the selected redirect rule.
If you want to disable the rule currently, you can switch it off from the left side. That will turn off the rule but will allow you to turn it back on at any point.